You are here
Back to topHow to Choose Thermal Pad
Modern electronic equipment is gradually moving towards miniaturization and lightweight design requirements, which has become a major development trend. Among them, how to achieve high-efficiency heat dissipation in a limited space has become a major development issue. The surface of most electronic components cannot be guaranteed to be completely smooth, so that there is a gap with the heat sink, and the thermal energy cannot be dissipated immediately. At this time, it is necessary to use thermal pads to fill the gaps to ensure that the conduction of thermal energy is not hindered. This article will discuss various thermal pads and how to choose a suitable thermal pad.
1. Prolegomenon
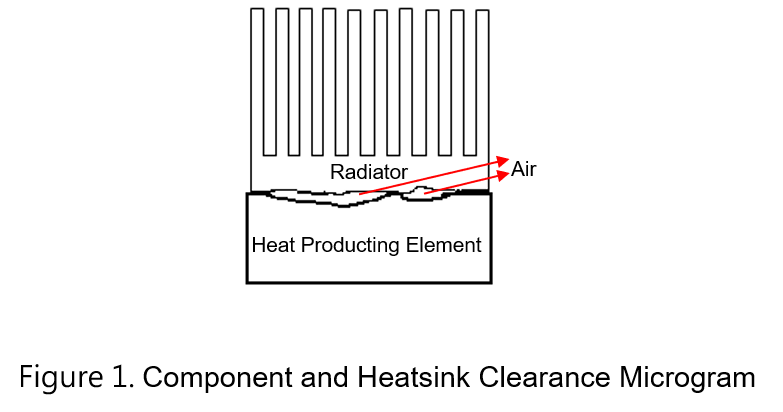
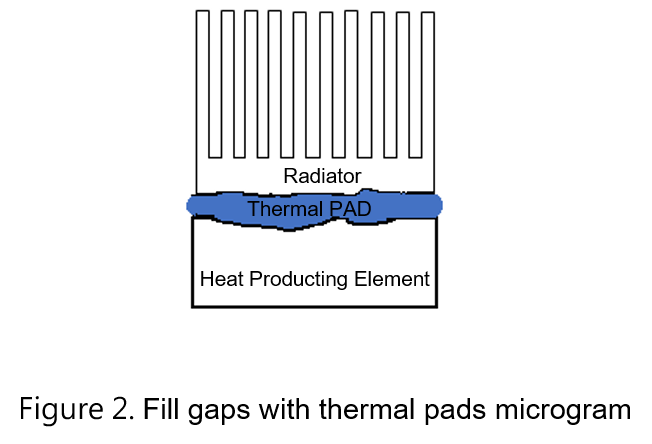
When the surface of the electronic material comes into contact with the heat sink, the voids in the contact surface can seriously hinder the conduction of thermal energy, as shown in Figure 1. Therefore, it is necessary to fill the gap through the thermal interface material such as thermal grease, thermal pads, etc., so that the thermal energy of the component can be more smoothly transmitted to the heat sink. Figure 2 shows a schematic diagram of using thermal conductive sheets to fill the gaps. The following will introduce the terms and explanations related to thermal pad.
- Thermal Pads
Thermal pads are solid products in Thermal Interface Material (TIM). Its main function is to fill the surface unevenness generated when the two materials are in contact and reduce the thermal resistance. Compared with Thermal Grease, it has the characteristics of convenient installation and disassembly and reusability.
- Thermal Conductivity
The parameter used to indicate the level of thermal conductivity(λ or K), and the unit is W/m·K. The thermal conductivity of common thermal pads ranges from 1 to 16, which is much larger than that of air, which is about 0.026 (W/m·K). It can be seen that the using thermal pads can effectively improve the thermal conductivity in the atmospheric environment. When selecting thermal pads, the thermal conductivity with the best performance is uncertain necessary, instead of thickness, hardness, and heat dissipation area will also affect the result of heat dissipation effect.
2. Types of Thermal Pads
Thermal pads can be classified into thermal with silicone and non-silicon. According to whether their material contains silicon or not, both are used in corresponding situations. The following will introduce the common types of thermal pads.
- Silicone Thermal Pads
The general silicone thermal pads already has the characteristics of insulation, compressibility, softness, etc., and the thermal conductivity mostly falls in 2 to 8 ( W/m· K), can effectively fill the gap between heating element and heatsink, to achieve to reduce thermal resistance, and then its thermal conductivity has adjustability, good thermal stability, so it is almost used in many conditions.
- Silicone High Thermal Pads
This type of pads is derived from the general silicone thermal pads, by adjusting the ratio of silicone and metal oxide, increasing the conductivity of silicone thermal pads, generally up to 10 (W / m · K). It is more suitable for filling between high-heat components and heatsinks than general silicone thermally pads.
- Glass Fiber Thermally Silicone Pads
When the thickness of the silicone thermally pads decreases, there is a risk of reduced toughness and rupture. At this time, the structural strength and insulating ability of the silicone thermally pads can be increased by adding glass fiber, making it suitable for use in harsh environments or occasions that require high insulation capacity, such as electric motors and vehicles, which work for a long time and frequently vibrate. However, its production process is more complex and the cost is higher.
- Non-Silicone Thermal Pads
This type of pad is a non-silicone-based thermal conductive material. Compared with silicone thermal pad, non-silicone thermal pad has a single type and higher cost, so the application field is less than that of silicone thermal pad. The main material is resin, which has the characteristics of high insulation, compressibility and softness. There is no problem of siloxane volatilization or silicone oil seeping, so it is suitable for sensitive areas to silicon, such as optical instruments, medical electronic applications, etc.
Sort out various types of thermal pads as shown in Table 1. According to the different components of thermal pads, make a comparison table of various characteristics.
| Silicone Thermal Pads | Silicone High Thermal Pads | Glass Fiber Thermally Silicone Pads | Non-Silicone Thermal Pads | |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m · K) | 1-8 | >10 | <5 | 1-8 |
| Insulation | Middle | Poor | Good | Good |
| Ductility | Middle | Good | Poor | Middle |
| Structural Strength | Middle | Poor | Good | Middle |
| Cost | Poor | Middle | Good | Middle |
3. How To Choose Thermal Pad
There are many types of thermal pads in the marketing, how to choose the suitable thermal pads is most important, the following will provide several aspects as the basis for selecting thermal pads.
- Gap Size
The size of the gap between the heating element and heat sink determines the thickness and ductility of the thermal pad that can be used. When the thickness of the thermal pad is thicker, its thermal conductivity will decrease. When the gap is less than 0.5mm, the thermal pad is at risk of cracking under high pressure, so the thermal pad with added glass fiber is used to increase the structural strength.
- Heating Area and Power
The area and power of the heating element determine the thermal conductivity of the thermal pads we selected. When the heating area is smaller and the power is greater, the thermal pads must be selected with a high thermal conductivity to maintain the heat dissipation effect.
- Insulation Requirements
Thermal pads should focus on the ability to withstand voltage, in the application of high voltage or power systems, you can use a silicone thermally pads with glass fibers to obtain higher insulation capacity.
4. Other Thermal Interface Materials
- Thermal Grease
Another name is thermal paste, which is paste-like at room temperature. The main component is silicone, and its insulation capacity is worse than the silicone thermal pad, and the thermal conductivity is close to the silicone thermal pads.
It is easy to contaminate the surrounding devices, difficult to reuse, the relative cost is low and the thickness is extremely thin. It is widely used in the occasions where the heating element needs to be closely attached to the heat sink.
- Thermal Putty
Thermal putty has some features, including excellent long-term reliability, physical properties between liquid and solid, the hardness falls between the thermal pads and the thermal grease, and high viscosity. It currently uses in a large number of automotive electronic production lines.
5. Conclusion
The choice of thermal pads on the market is quite diverse, whether it is the general type, high thermal conductivity type, glass fiber type, or non-silicon thermal conductive pads designed for silicon-sensitive circuits, which can improve the thermal conductivity of the heating element to the heat sink. The selection of thermal pads is not the higher the thermal conductivity, but the most suitable thermal pads are selected according to the needs of thickness, hardness, heat dissipation area, insulation, etc.
CTC is service provider for high-end power modules (DC to DC Converter and AC to DC Converter) for critical applications worldwide since 1987. We aim to be business generator and a virtual business unit. CTC is your own team with 35 years of experience for a strong business program from market research, product definition & development, supply chain management and total technical services.
CTC is the only corporation certificated with ISO-9001, IATF-16949, ISO22613(IRIS, AFNOR silver certificate), and ESD/ANSI-2020. We can 100% ensure not only the product, but also our workflow and service to match quality management system for every high-end application from the very beginning. From design to manufacturing and technical support, every single detail is operated under highest standard.

