You are here
Back to topIntroduction of Reliability Verification – Vibration Test
In recent years, the production process of power converters has been required to meet high-reliability military standards (MIL-STD), which consider test environments such as high/low temperatures, humidity, vibration, and shock to ensure proper operation in extreme conditions. This article introduces the vibration tests of MIL-STD-810 and MIL-STD-202, while comparing the similarities and differences in vibration procedures for different shipping methods.
Introduction
During the transportation process, power converters are subject to various vibration amplitudes and frequency ranges, which can lead to component loosening or relative movement between components, resulting in abnormal noise, mechanical wear, and physical deformation, which are undesirable for both manufacturers and users. Strengthening packaging or changing transportation methods may prevent damage during shipping and reduce returns but will increase production costs and reduce market competitiveness. Therefore, conducting vibration tests before shipping power converters is essential.
The purpose of vibration testing is to simulate various vibration conditions to assess whether the power converter can withstand the vibrations encountered during transport. If the electrical characteristics cannot be maintained during vibration tests, defective units must be filtered out, and the causes of failure evaluated. Depending on the environmental conditions, vibration tests typically include sinusoidal vibration tests, random vibration tests, or a combination of both.
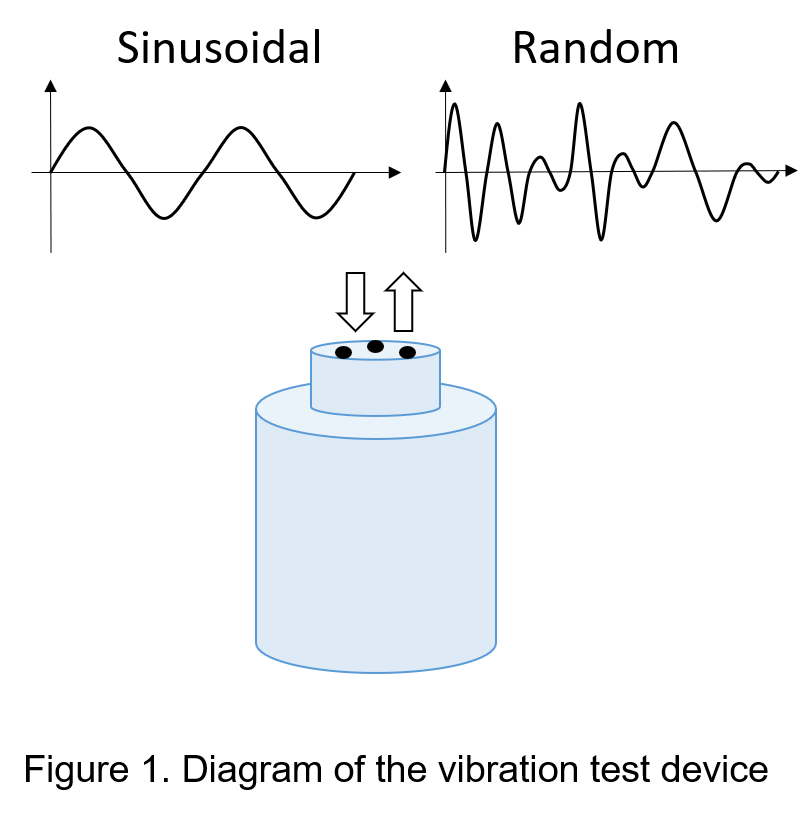
For general industrial applications, sinusoidal vibration tests are often sufficient, but random vibration tests provide a more realistic simulation of vibrations experienced in various scenarios, such as cars traveling on uneven roads, ships navigating at sea, and jets during flight.
Vibration Test of MIL-STD-810 and MIL-STD-202
Military equipment must operate reliably in extreme environments, so the test items covered by military standards are required to meet stringent criteria. MIL-STD tests must be conducted by certified laboratories, with MIL-STD-810 being one of the most widely adopted standards and MIL-STD-202 focusing on electronic and electrical component testing. Below are the vibration test procedures for both standards.
1. MIL-STD-202
(1) Vibration Test
Conducted using test method 201, the appropriate equipment must be selected, and the product installed according to specifications to avoid resonance within the test frequency range.
This test involves simple harmonic motion with a maximum displacement of 0.06 inches, with a uniform frequency variation from 10 to 55 Hz and back to 10 Hz within approximately one minute, vibrating along three axes for two hours each.
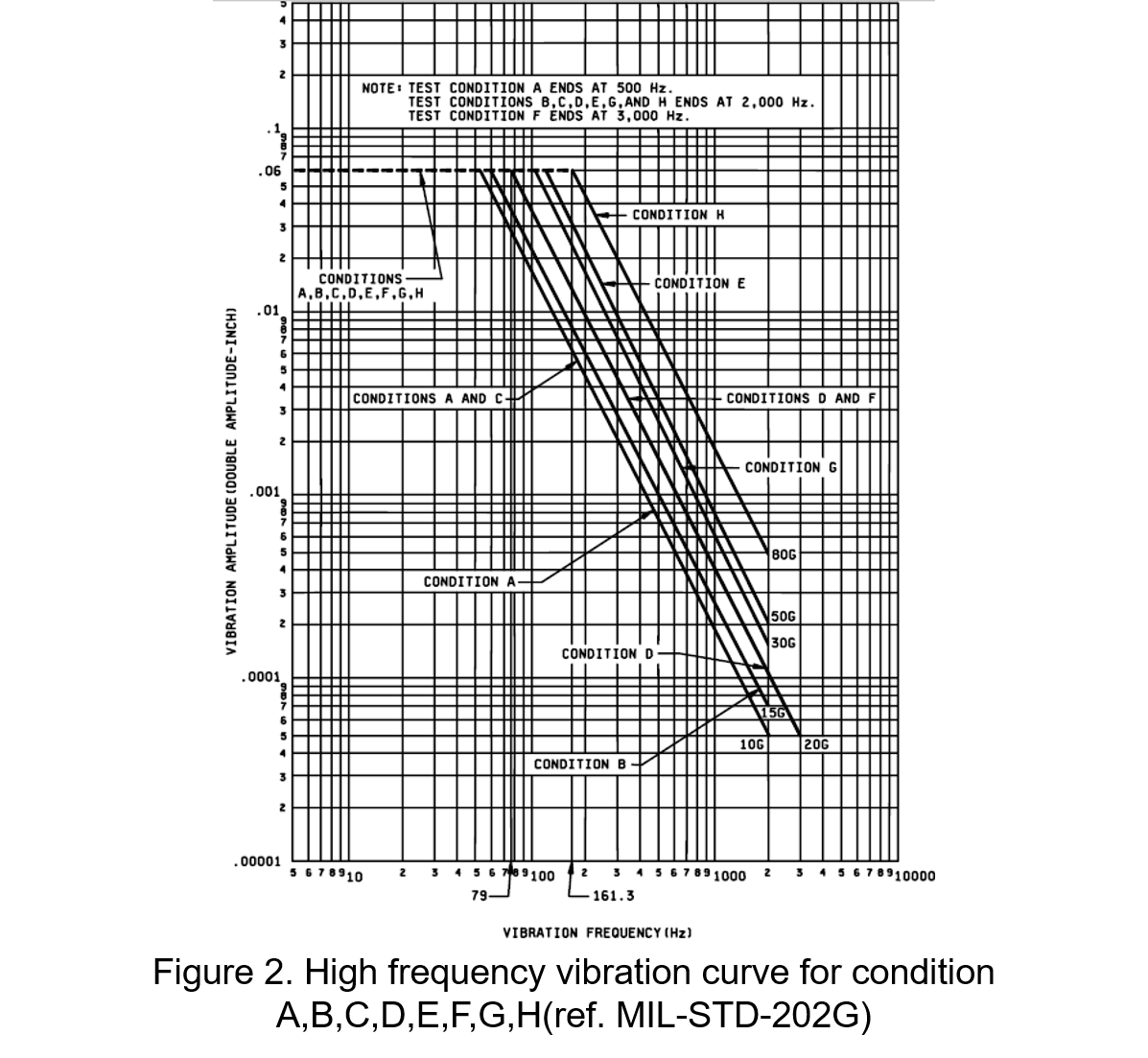
(2) High Frequency Vibration Test
Conducted using test method 204, this test evaluates the impact of vibration frequencies ranging from 10-500 Hz, 10-2000 Hz, or 10-3000 Hz on components, such as those used in aircraft or missiles. According to the specified frequency range, amplitude, and duration, the test can be divided into eight conditions: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H. Samples must be tested under power-off or specified load conditions. Figure 2 shows the high-frequency vibration test curve.
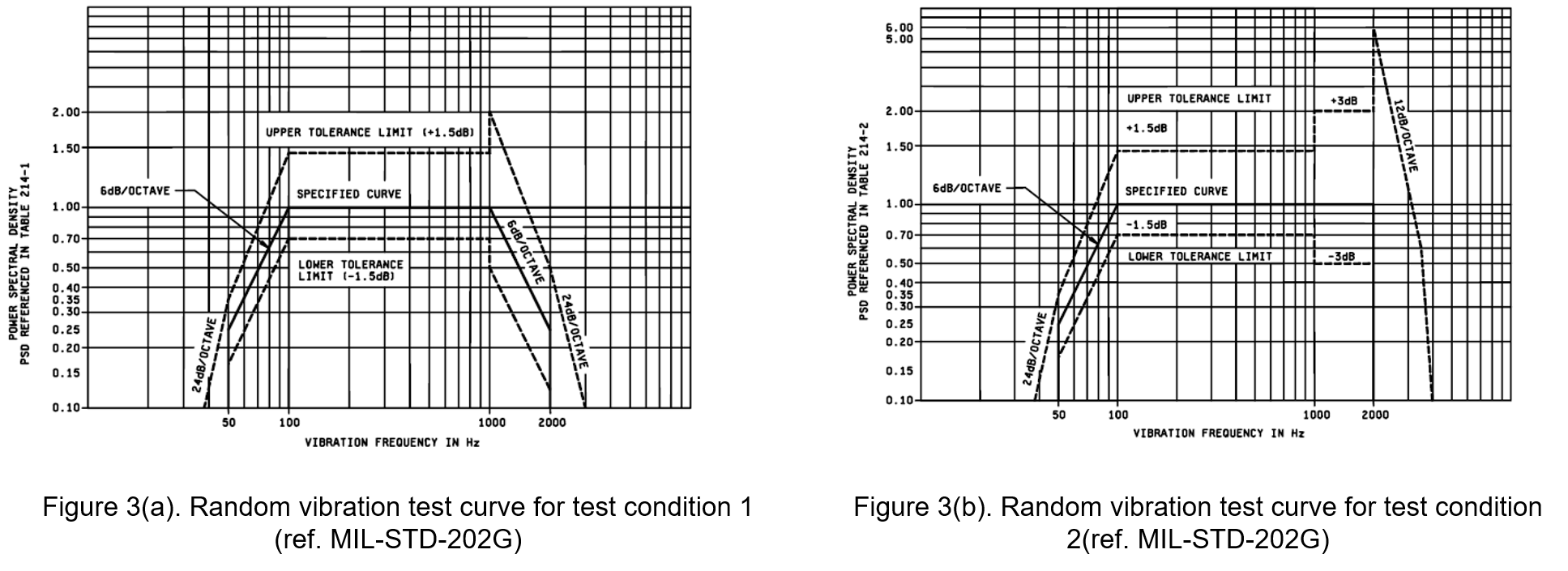
(3) Random Vibration Test
Conducted using test method 214, this test primarily determines the dynamic stress exerted by random vibrations within the upper and lower frequency limits on components, such as those experienced in jet aircraft and rocket engine environments. The amplitude of the random vibration follows a Gaussian distribution, with peak acceleration limited to three times the root mean square of the minimum value.
When the test item is mounted and monitored on a military vibration system, the fixtures should be installed as close as possible to the item's mounting points to facilitate monitoring of the vibration amplitude. When measuring the vibration input at multiple points, the minimum input vibration usually corresponds to the specified test curve, as shown in Figure 3, with the amplitude of the power spectral density curve falling within the designated limits of the vibration system.
2. MIL-STD-810
MIL-STD-810 is a military testing standard aimed at determining vibration amplitude and life cycle duration to verify whether products can withstand vibration exposure and be developed to operate in various application environments.
MIL-STD-810 includes four procedures under vibration method 514, each focusing on specific applications and aiming to simulate vibration conditions in environmental life cycles as accurately as possible.
(1) General Vibration: Applies to systems fixed on transport vehicles.
(2) Loose Cargo Transportation: Simulates military vehicles transporting loose, unsecured cargo over rough terrain.
(3) Large Assembly Transportation: Simulates the vibration environment for transporting large material assemblies.
(4) Assembled Aircraft Transportation and Free Flight: Applies to the transport of fixed-wing aircraft and the free flight phase of missiles.
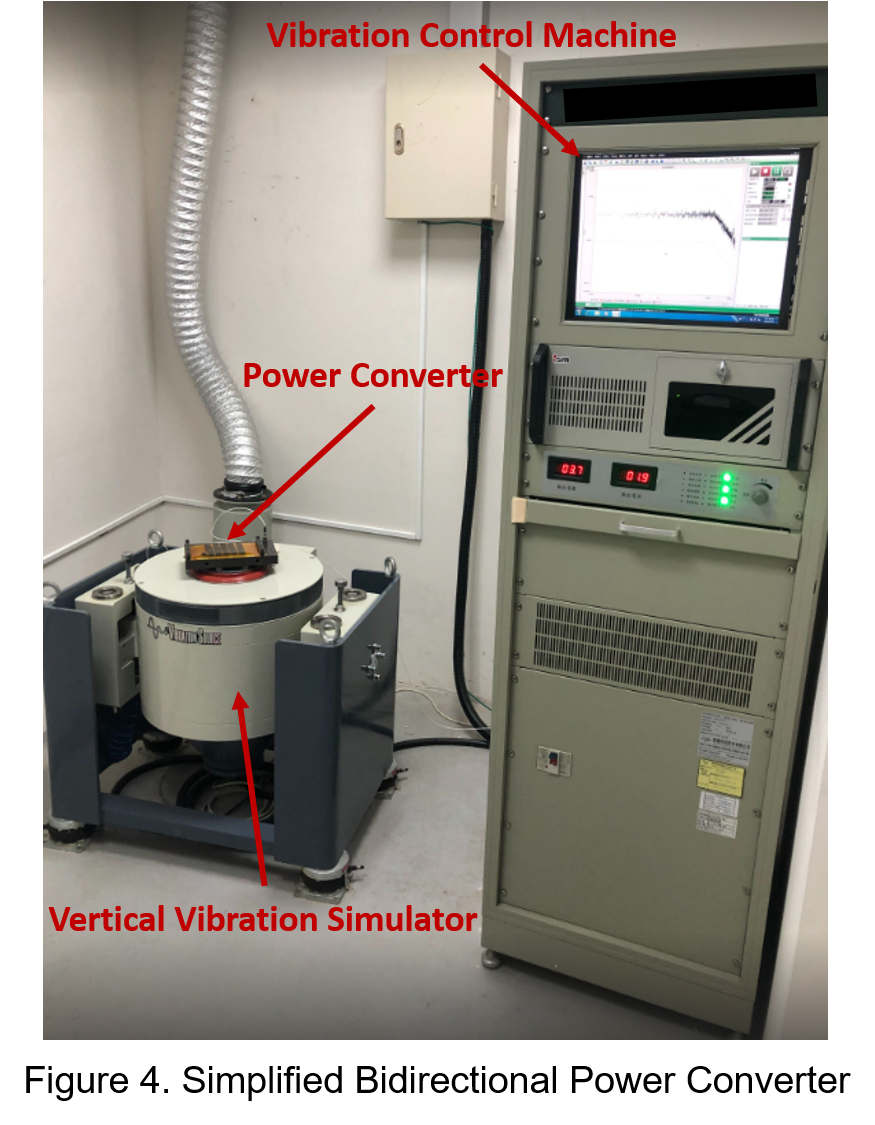
A military-grade vibration testing machine is selected to simulate extreme vibration environments, testing the intensity of vibrations and the reliability of power converters in various application fields. This includes verifying electrical functionality, instrument precision, and ensuring that power converter pins remain intact and package joints are not damaged.
The diagram below shows a vertical vibration testing system. First, the power converter is fixed onto the vibration platform, where the vibration control machine applies various vibration waveforms, such as sinusoidal and random tests, while controlling parameters like vibration frequency, amplitude, speed, acceleration, and duration.

3. Corresponding Vibration Environment
For various application environment tests, appropriate standards are selected and applied based on the MIL-STD-810 specifications. These applications include cargo on trucks/trailers, jet aircraft, helicopters, airplanes, ships, and trains. The discussion covers the vibration conditions, duration, and acceleration spectral density plots for cargo in each application. However, MIL-STD-202 only addresses vibration testing, installation methods, and vibration duration, without specifying particular application conditions.
The following provides a brief discussion on the vibration conditions for air transport cargo as outlined in MIL-STD-810 and how these correspond to the testing conditions of MIL-STD-202.
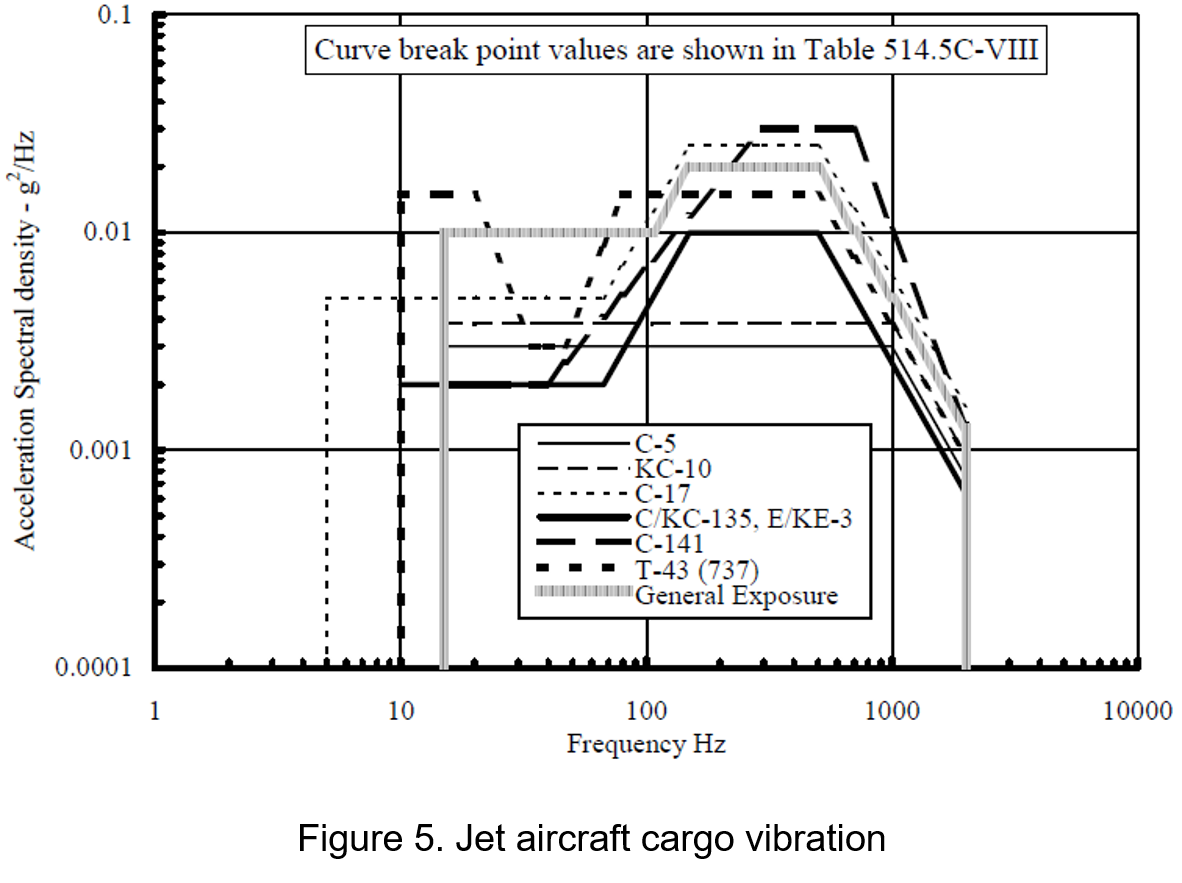
(1) Application - Jet Aircraft
The purpose of this test is to determine the ability of electronic components to withstand random vibrations during transportation, simulating various scenarios. For example, the maximum vibration in jet aircraft is produced by engine exhaust, especially during takeoff.
|
Application-Jet aircraft |
MIL-STD-810 |
MIL-STD-202 |
|
Describe |
Method 514.8 General exposure: The recommended criteria for jet aircraft cargo, and broadband random |
Method 214 Characteristic of modern field environments produced by missiles, high-thrust jets and rocket engine |
|
Items |
1.Frequency: 15-2000Hz |
1.Frequency: 50-2000Hz |
|
2. Exposure Duration Time: 1 minute per takeoff |
2.Duration Time: The specimen shall then be subjected to the vibration specified by figure 5 for the duration as specified in the individual specification: 3-minutes; 15-minutes; 1-1/2 hours; or 8-hours |
|
|
3. Acceleration Spectral Density: max. 0.02 g2/Hz |
3. Acceleration: The magnitudes of peak values may be limited to a minimum of three times the rms (three-sigma (σ) limits) |
|
|
4.Curve: Figure 6 |
4.Curve: Figure 3(a)(b) |
Conclusion
High-reliability electronic products must undergo vibration tests after design to effectively screen out defective units early and prevent damage during transportation.
CTC is service provider for high-end power modules (DC to DC Converter and AC to DC Converter) for critical applications worldwide since 1987. We aim to be business generator and a virtual business unit. CTC is your own team with 35 years of experience for a strong business program from market research, product definition & development, supply chain management and total technical services.
CTC is the only corporation certificated with ISO-9001, IATF-16949, ISO22613(IRIS, AFNOR silver certificate), and ESD/ANSI-2020. We can 100% ensure not only the product, but also our workflow and service to match quality management system for every high-end application from the very beginning. From design to manufacturing and technical support, every single detail is operated under highest standard.

